A resistive touch screen is a sensor that converts the physical location of a touch point (X,Y) in a rectangular area into a voltage representing the X and Y coordinates. Many LCD modules use resistive touch screens. Resistive touch screens can be divided into four-wire, five-wire and other multi-wire resistive displays according to their structures. Four-wire resistive displays are the more common one. This chapter will focus on the working principle of the four-wire resistive touch screen.
How resistive touch screens work
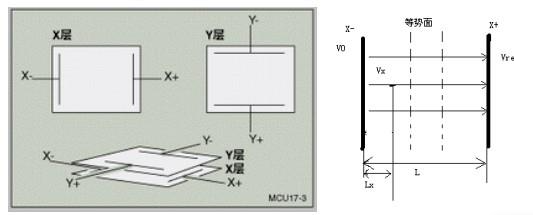
Resistive touch screens mainly operate and control screen content through the principle of pressure sensing. This touch screen uses two layers of highly transparent conductive layers to form a touch screen. When a finger touches the screen, the two conductive layers that are usually insulated from each other are There is a contact at the touch point position, because one of the conductive layers is connected to a 5V uniform voltage field in the Y-axis direction, causing the voltage of the detection layer to change from zero to non-zero. After the controller detects this connection, it performs A/ D conversion, and comparing the obtained voltage value with 5V, the Y-axis coordinate of the touch point can be obtained. Similarly, the X-axis coordinate can be obtained. This is the most basic principle common to all resistive technology touch screens.
How a four-wire resistive touch display works
When a person's finger presses the touch screen surface, the elastic PET film will bend downward, allowing the upper and lower ITO coatings to contact each other to form a touch point. An ADC is used to detect the voltage at this point to calculate the X and Y axis coordinate values.
The working principle of the four-wire resistive touch screen is as follows:
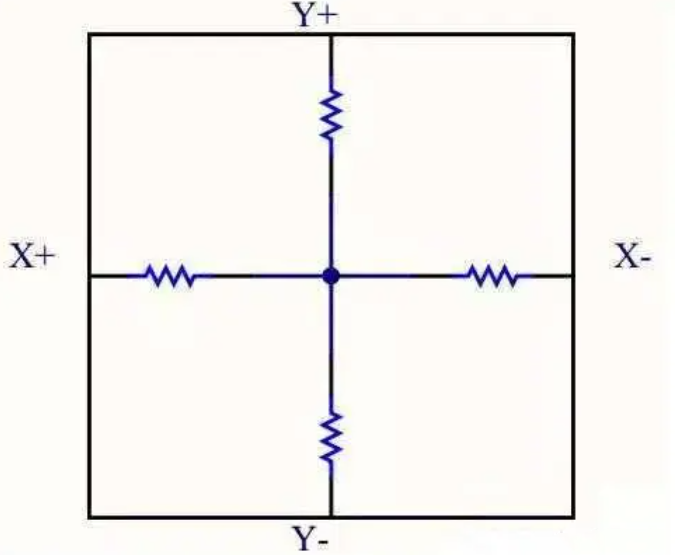
1. Add a constant voltage Vref to the X+ and X- electrodes, and connect Y+ to a high-impedance ADC.
2. The electric field between the two electrodes is uniformly distributed in the direction from X+ to X-.
3. When the hand touches, the two conductive layers come into contact at the touch point, and the potential of the X layer at the touch point is directed to the ADC connected to the Y layer.
Get the voltage Vx.
4. Through Lx/L=Vx/Vref, the coordinates of the x point can be obtained.
5. In the same way, connect Y+ and Y- to the voltage Vref, the coordinates of the Y-axis can be obtained, and then connect the X+ electrode to the high-impedance ADC to obtain. At the same time, the four-wire resistive touch screen can not only obtain the X/Y coordinates of the contact, but also measure the pressure of the contact.
This is because the greater the pressure, the more complete the contact, and the smaller the resistance. By measuring the resistance, the pressure can be quantified. The voltage value is proportional to the coordinate value, so it needs to be calibrated by calculating whether there is a deviation in the voltage value of the (0, 0) coordinate point.

Hot Display supports customized resistive functions and touch screens, please contact us!