制作液晶显示器除了主要材料之外,还需要辅助材料。辅助材料是指产品生产过程中使用而最终产品中不存在的原材料,主要包括光刻胶及其稀释剂、P稀释剂、NMP、BC 液、Si0,稀释剂、摩擦布、异丙醇、乙醇、丙酮、清洗剂、酸、碱等。
1.光刻胶
光刻胶又称感光胶,一般由感光剂(光致抗蚀剂)、增感剂和溶剂组成。感光剂是一种特别敏感的高分子化合物,当它受到适当波长光照射时,能吸收一定的光能量,使之发生交联聚合或分解等光化学反应,使光刻胶改变其性能。
1)光刻胶的分类
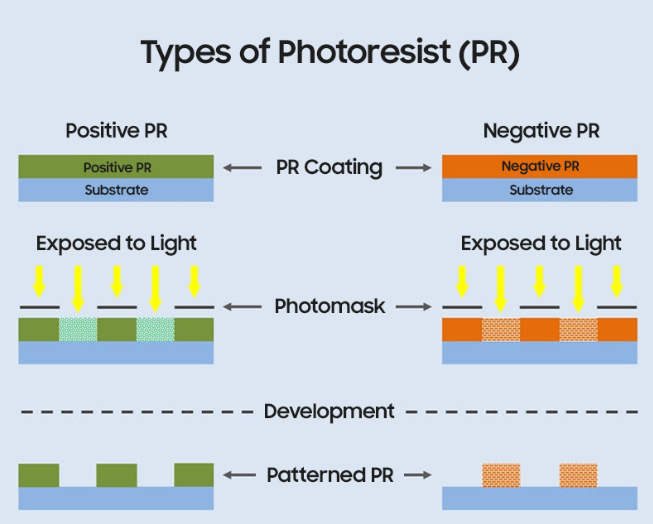
光刻胶是光刻工艺的主要材料,光刻胶种类很多,目前国内外的光刻胶品种已达40多种据光刻胶曝光前后溶解度特性的变化,可将光刻胶分为正性胶和负性胶两大类。
负性胶在曝光前对某些有机溶剂(如丙酮、丁酮、环己酮等)是可溶性的,曝光后发生光聚合反应,不溶于有机溶剂。当用它进行光刻时,在衬底表面将得到与光刻掩模版遮光图案完全相反的图形,故称为负性胶。
正性胶在曝光前对某些溶剂是不可溶的,而曝光后却变成了可溶的。使用这种胶光刻时能得到与光刻掩模版遮光图案相同的图形,故称为正性胶.
正性光刻胶和负性光刻胶光照后图形变化示意图如图一所示:
(图一)
2)光刻胶的主要技术指标光刻胶性能的好坏对光刻质量影响很大,习惯上常用感光度、分辨率、抗蚀性、黏附能力和针孔密度等指标来衡量其优劣。
(1)感光度:
感光度是一个表征光刻胶对光敏感的性能指标。感光度不同,表示它对光的敏感程度不同,即光化学反应所需的曝光量不一样。
对于某固定光强的曝光机,光刻胶的感光度越高,则曝光时间越短;反之,则曝光时间需相应加长。
(2)分辨率:
分辨率是表征光刻胶的光刻精度的标志之一。它不仅与光刻胶本身有关,还与光刻工艺条件和操作技术因素有关。
(3)抗蚀性:
通常要求光刻胶对酸、碱化学腐蚀液具有良好的抗蚀能力,即能经受得住较长时间的酸碱腐蚀液的浸蚀。实际上,光刻胶只是在针孔密度小、黏附性能良好的情况下,才可能有较好的抗蚀能力。
(4)黏附能力:黏附能力表示光刻胶与衬底之间黏附的牢固程度,它直接影响光刻后的精度。光刻胶的黏附力不仅与光刻胶的本身性质有关,而且与衬底的性质及其表面情况有密切关系,平整、致密、清洁、干燥的衬底表面有利于光刻胶的黏附。此外,光刻胶的配比、前烘条件和显影液配方等因素也都会影响光刻胶的黏附性。
(5)稳定性:
生产上要求光刻胶具有一定的稳定性,即要求光刻胶在常温和光(主要是紫外光)屏蔽的情况下,光刻胶不应发生暗反应。要求光刻胶杂质含量少,显影后无残渣。
(6)针孔密度:单位面积的光刻胶膜上针孔数目称为光刻胶膜的针孔密度。要求光刻胶膜的针孔密度尽可
能低。
(7)黏度和固态含有率:光刻胶的黏度和固态含有率是影响涂覆胶膜厚度的主要因素。光刻胶越浓,它的黏度就大(即越稠),在相同涂胶条件下,所得到的胶膜就越厚;反之,则黏度小,胶膜薄。因此,可以通过改变胶液的浓度来调节胶的黏度,进而控制胶膜的厚度。
其他辅助材料
其他辅助材料包括液体材料浓盐酸、浓硝酸、氢氧化钠、清洗液、乙醇、丙酮及各种版网,以及其他辅助工具。这些材料在液晶显示器的生产过程中也起着非常重要的作用。这些辅助材料的作用如下:
(1)浓盐酸、浓硝酸用于腐蚀无光刻胶覆盖的 TTO 膜。
(2)氢氧化钠用于ITO玻璃的清洗,去除玻璃表面的杂质;用于光刻时的显影液,溶除未感光部分的光刻胶;用于光刻后的去胶,将经过腐蚀的玻璃表面的光刻胶去除干净。
(3)清洗液用于去除玻璃表面及两片玻璃间隙中的有机杂质,包括异丙醇及其他类型清洗液等。
(4)乙醇、丙酮主要用于擦除液晶屏表面杂质,以及容器的清洗等。
(5)菲林版是通过制版方法在胶片上制成与电极图形对应的黑白图案,曝光时,使透明区光刻胶在光的作用下起反应。
(6)APR版用于选择性涂覆取向层(PI和Si0,)。
(7)丝网用于丝印成盒时,漏印封框胶及导电胶。
(8)摩擦布用来使液晶分子排向,即通过摩擦布绒毛与玻璃表面的取向摩擦,使玻璃表面产生许多沟槽。
(9)切割刀轮在精密切割机上使用,材料为金刚砂,用于在玻璃表面划出刀痕。
推荐文章:液晶显示器主要用到什么材料?