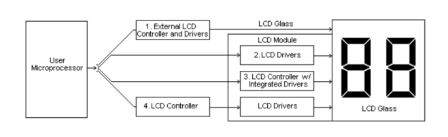
Fig. 1 Connection Between MCU to LCD
LCD can’t be driven with DC (Direct Current), it has to be driven with AC (Alternative Current) and the overall current has to be ZERO. Otherwise, the Liquid Crystal Material will be damaged sooner or later.
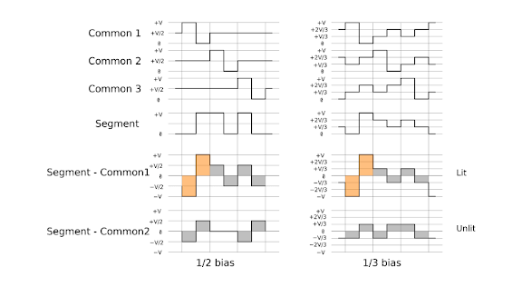
Fig. 2 LCD Driving Waveform
There are two types of Driver IC’s, Common Drivers and Segment Drivers. Common Drivers output signals to create the rows or numbers of lines. The Segment Drivers output the necessary signals to create the characters or columns.
The Controller IC receives data written in ASCII or JIS code from the MPU and stores this data in RAM. This data is then converted into serial character patterns and transferred to the LCD driver IC.
Drive/Controller IC is probably the most commonly found in a graphics module. This IC receives data from the MPU and stores it in RAM. Also, it accepts commands directly from the MPU for both the common and segment drivers.
RGB interface often been used in control large-scale high-resolution LCD display. It include 6/16/18bits data (like R0, R1, , , G0, G1, , ,B0, B1, , , ), VSYNC (Vertical synchronization), HSYNC (Horizontal synchronization).
Advantage is that R,G,B data is written to LCD directly without GRAM, high speed. Normally used in large-scale high-resolution LCD.
Disadvantage is to control LCD is more complex, and need more data wires than MCU interface.
Application: Medium size TFT (3.5” to 8”)
RGB interface includes 24 bit, 18 bit, 16 bit

Fig. 3 RGB Interface

Fig. 4 Examples of 24 Bit and 18 Bit RGB Interface
For RGB Interface related products, you can also find it here.